QnA: ALTERNATORS / GENERATORS
List of FAQ on Alternators that every ETO must know.
Q. If two generators running in parallel KW are same but ampere is different. what reason, how to correct it?
A. Simple method of power corrections. At no load adjust the voltage of each generator to within plus / minus 2. Lock VR potentiometer firmly all power factor and load sharing problem will be resolved. Less power factor will draw more current. KVAR is equally shared when ammeter readings are the same.
Q. What is armature reaction?
A. When the current flows through the armature winding of the alternator resulting MMF is produced which in turn produces flux. The armature flux reacts with main pole flux either to increase or decrease resultant flux. The effects of armature(stator) flux on the flux produced on rotor field is called Armature reaction.
Q. Why alternator power rating is mentioned in KVA?
A. Power factor is different for different load conditions so KW cannot be predicted so maker mentions power rating in KVA.
Q. Why stator air gap of a alternator is more than that of exciter air gap?
A. An increase in air gap increases the reactance of the motor lower its power factor. In synchronous DC machines, two separate fields interacting with the air gap. The AC field created by armature(stationary in the synchronous machine, rotating in dc machine) that distorts that supplied by the DC field, reducing its effectiveness and degrading machine performance. Increasing air gap minimize armature reaction. Therefore these machines will have air gaps several times larger than induction motors.
Q. Why Reverse Power used instead of Reverse Current in alternator?
A. It is difficult to detect reverse current with alternator current system, reverse power can be detected and protection can be provided by reverse power relay.
Q. Why zener diode is used in alternators AVR?
A.
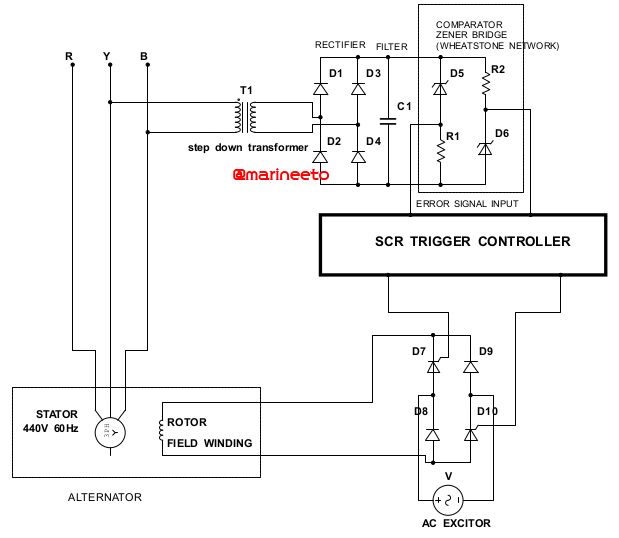
The Zener operate in the reverse breakdown mode, as these diodes are manufactured with a Zener breakdown voltage of very low value. Zener diode voltage remains constant once breakdown voltage has occurred despite the change in the current. This implies that changes in applied voltage, while not affecting voltage across the diode, will cause a change in resistance which permits the change in current. As with a Wheatstone bridge, imbalance of the resistance changes the flow pattern and produces in the voltage measuring bridge an error signal.
Q. What is droop?
A. The drop in voltage/RPM from no load to full load is known as droop. There are two types of droop :
i) Governor droop: is to maintain KW during paralleling thus maintaining constant RPM. when droop setting of both generator same it ll share equal load. Generator which has less droop will share more load.
ii) AVR droop: it corresspond to KVAR. AVR which has less droop will have more lossess will increase. Power factor will drop efficiency will decrease.
Q. Two generators are running parallel. One needed to be offloaded but ACB not tripping due to mechanical fault. Whats your action?
A. If unable to carry OFFLOAD in auto mode, next step try it in MANUAL mode i.e., reduce load switch off ACB. If it is not possible then the local button on ACB should be used. Even if that is not possible then you have to do BLACK OUT ensure bus bar is dead. Physically examine ACB, inspect contacts which should be brazed thats why unable to open contacts.
Q. What will be effect on switchboard voltmeter when you increase the voltage of one generator by voltage trimmer?
A. The AVR voltage output may be adjusted with hand regulator. Increasing/Decreasing the excitation on one generator will change only the power factor on that unit. If generator is over excited the voltage cannot increase due to the grid but the generator will take more of the load.
Q. How to do flashing or Restoring Residual Magnetism in field coil?
A.
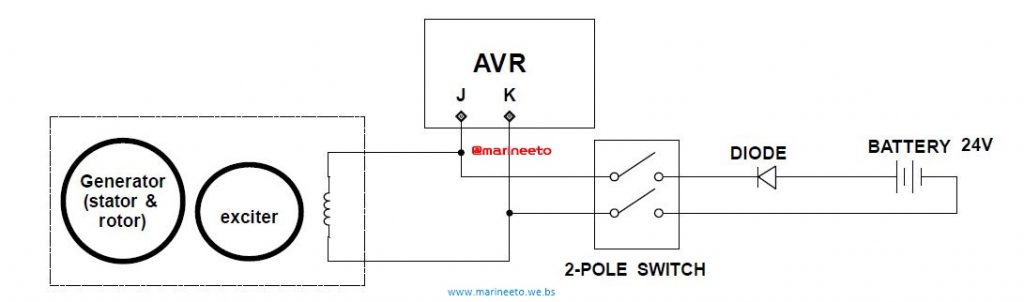
Connect DC24V as shown in circuit diagram connecting +ve to J of AVR and -ve to K of AVR input to field windings of exciter with generator stationery. Keep the switch closed to supply DC to the field coil for 2 minutes. This should restore residual magnetism.
Q. What happens if rotating diode in alternator fails (cross questions)?
A. Failure Mode: One shorted diode.
(This is the most common mode of diode failure in brushless generator rotating rectifier assemblies.)
Cause: Over voltage or current. Usually due to out of phase paralleling, a lightning strike or other abnormal transient. This mode of diode failure may also occur if a voltage is imposed upon the terminals of a brushless generator while it is at rest.
Effects: Increased excitation. Exciter rotor and/or voltage regulator failure likely. The exciter rotor may fail due to excessive current, which may occur within seconds depending on load level trying to be achieved. The voltage regulator may fail due to high voltage ripple reflected back through the exciter field (stator). If the voltage regulator is equipped with an over excitation trip feature, these failures may occur before the voltage regulator trips out on over excitation. The generator may be able to maintain a light level of loading without noticing the problem.
Failure Mode: One Open Diode.
Cause: After a diode shorts, it will burn open if no other failure occurs first. There may actually be a broken or loose connection external to diode which will have the same effect as an open diode even though the diode itself has not failed open.
Effects: Increased excitation. Will overload other diodes and exciter rotor winding eventually depending on load. Does not typically cause regulator failure. If the voltage regulator is equipped with an over excitation feature, it may be activated depending onload, regulator compatibility, and the over excitation feature set points.
Failure Mode: Multiple Shorted Diodes.
Cause: The same as for a single shorted diode.
Effects: The same as for a single diode failure except that it is unlikely that the generator will be able to maintain open circuit voltage. Almost certain exciter rotor failure if not shut down immediately.
Failure Mode: Multiple Open Diodes.
Cause: The same as for a single opened diode.
Q. How shaft current is generated. What are the effects and How to overcome it?
A. Machines with very strong magnetic field often generates a voltage in shaft that generates Shaft Current. Shaft Current flow through bearings cause an electrolytic reaction which will cause bearing failure in due course and possible sludging of lubricating oil. To eliminate shaft current either bearing shell is insulated in the housing or outboard pedestal bearing is insulated from the foundation.
Q. How insulation of pedestal bearing is checked?
A. The pedestal insulation of dismantled generator is tested using meggar with minimum reading of 20KiloOhms and above is considered as satisfactory.
Condition can also be checked while machine running by measuring millivolts between shaft and bedplate. One with jumper connected to shaft and pedestal and Other one without jumper. If insulation is good both reading would be almost same. If defective reading one will be higher than other.
LIKE POST PLEASE SHARE, COMMENT
















Really informative
Thank You Kevin, for your comment.
Like our Facebook page for more updates
Excellent, few more questions on many other concepts would be helpful