QnA: INDUCTION MOTOR
Hello everyone, In this post we are sharing list of QnA about Induction Motor which was collected during COC exams. Hope this post will help you out.
Q. Why the induction motor is called asynchronous motor?
A. Since the induction motor runs always at a speed lesser than synchronous speed, it is called asynchronous motor.
Q. What is Slip?
A. This difference between the speed of the rotor and speed of the rotating magnetic field in the stator is called slip. It is unitless and is the ratio between the relative speed of the magnetic field as seen by the rotor to the speed of the rotating field. Due to this an induction motor is sometimes referred to as an asynchronous machine.
Q. What is crawling and cogging of an induction motor?
A. CRAWLING is the phenomenon in which motor operates at very low speed. Crawling is caused by the presence of space harmonics in the air gap flux. Following are the reason for the presence of space harmonics in the air gap flux.
- Air gap harmonics due to uneven distribution of Stator winding.
- Due to variation in air gap reluctance because of Stator and Rotor Slots. Space Harmonics due to this is also called Slot or Tooth Harmonics.
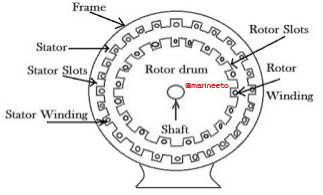
COGGING is the phenomenon in which number of stator slots is equal to or an integral multiple of the rotor slots, the motor may refuse to deliver the torque because of the magnetic locking between the stator teeth and rotor teeth caused by the minimum reluctance.
The reluctance is minimum when the stator slots are equal to or an integral multiple of the rotor slots. The phenomenon of magnetic locking created between the stator and the rotor teeth is called the cogging. The phenomenon of cogging can be avoided by taking an appropriate combination of the stator and the rotor slots while designing the motor. The cogging in induction motor is undesired phenomenon.
Q. What is skewing ?
A. The arrangement of slots of rotor is angled with the axis of shaft is called skewing.

The effect of skewing will slightly increase the rotor resistance and increases the starting torque. However this will increase the leakage reactance and hence reduces the starting current and power factor.
Q. Assume that Rotor and Stator slots are equal. How will you prevent clogging?
A. Other way to prevent cogging is skewing of rotor bars.
The teeth of the rotor and stator never be made equal because of to rotate the Induction Motor needs the relative speed between the stator rotating magnetic field and rotor when the relative speed is zero the motor starts decelarate and cannot turn the motor.
Q. What happens if supply voltage is reduced by 10% to induction motor?
A. The starting torque of the motor is reduced approximately by 20%. Torque is directly proportional to the square of voltage. Let the reduced voltage be V. Then, V=V-10%V =V-0.1V =0.9V. T will be proportional to (0.9V)^2 i.e., 0.81V. Thus, torque is reduced by 100-81= 19% say 20%
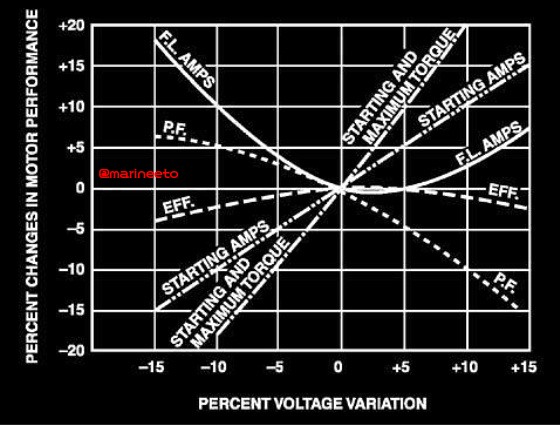
From the graph it is also seen 10% reduced in voltage also affects increase in power factor, increase and decrease in full load current as we increase and decrease voltage thus motor can run hotter due to losses if it exceeds design value.
Q. What happens when 50Hz induction motor is made to run at 60Hz?
A. The following effect can occur. The main thing V/f(Volatge/frequency) ratio must be maintained.
- Speed is directly proportional to frequency. speed of motor exceeds rated speed. From this formula Ns=120f/p for a 50Hz, 3 pole motor speed is 2000 RPM and for a 60Hz, 3 pole motor speed is 2400 RPM. Its almost 20% raise from rated speed.
- Bearing life is reduced due to speed more than rated speed.
- Power factor is reduced due to an increase in core losses which also cause overheating of the core. (Frequency is directly proportional to inductive reactance so an increase in reactance means increased reactive power by formula PF=true power/apparent power=R/Z).
Q. What happens when 60Hz induction motor is made to run at 50Hz?
A. Motor runs slower. If the frequency is reduced even voltage must be reduced to keep V/f ratio. If we run at same rated voltage for 60Hz then we are overexciting it. The core will saturate and magnetizing current will be high will damage the motor.
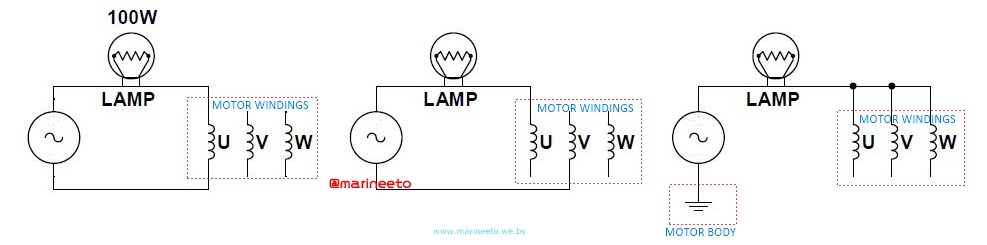
Q. How will you check motor if you do not have Multimeter and Meggar?
A. Continuity of winding and Health of insulation can be checked using SERIES LAMP TEST METHOD. Only drawback you will not get to know the value of insulation resistance but Short Circuit, Open Circuit and Continuity can be tested.
Q. What happens if airgap of induction motor is increased?
A. Increase in airgap increases iron losses therefore efficiency decreases.
Q. When will induction motor have maximum torque?
A. When rotor resistance per phase is equal to rotor reactance per phase under running condition.
Q. What Is Commutator?
A. Commutator is an electrical switch that periodically reverses the current direction in an electric motor or electrical generator. A commutator is a common feature of direct current rotating machines. By reversing the current direction in the moving coil of a motor armature, a steady rotating force (torque) is produced. Similarly, in a generator, reversing of the coil connection to the external circuit produces unidirectional current in the circuit.
Q. Why Capacitor is used in Single Phase Induction Motor?
A. The magnetic field in a single phase AC motor is not rotating, thus the motor is not self-starting.
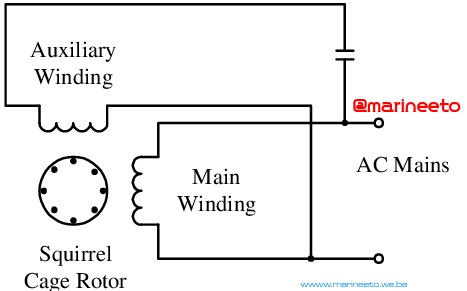
Creating a phase difference between the current in the main coil and that in the auxiliary coil so that as the current alternates in both of them we get a total rotating magnetic field. Current in capacitive circuits lead voltage. For the same voltage in the main and auxiliary coils, the current in the auxiliary winding leads that in the main winding (by 90 degrees).
Q. Types of Single phase Induction motor?
A. The single phase induction motors are classified as
- Split phase induction motor.
- Capacitor start inductor motor.
- Capacitor start capacitor run induction motor (two value capacitor method).
- Permanent split capacitor (PSC) motor.
- Shaded pole induction motor.
LIKE POST? PLEASE SHARE
















thanks for valued shared knowledge of your link.. i really interested for electrical due i am not electrical Engr. just a vocational skill.. although im very thankfull for this you giving source of educational knowledge of skill
Thank You Rolando Cinco for sharing your feedback.
We appreciate your interest in electrical engineering.
Keep supporting us.
Like our social page to stay updated.