MARINE CABLE COMPLETE GUIDE
There is an extensive variety of marine cables based on specification, type of use that consolidates power, control, signal, and instrumentation. Marine cables are expected to perform under extreme conditions like Temperature(High and Low), Vibration, Corrosive materials, Saltwater, etc. They must also meet international standards too. In this post, we will describe more about marine cables.
What are the specifications you consider while buying electric cable?
When selecting a cable or wire for an application, make sure that you consider all the factors mentioned below
• Insulation- To select the right insulation, you should know the maximum temperature to which the cable will be exposed to. Whether it will be exposed to chemicals, oils or manufacturers should also be taken into consideration. For Example: Insulation for high voltage cable is XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene) & have longer life compared to PVC(Poly Vinyl Chloride).
• Conductors- Will the material be tinned, bare, copper plated, or maybe bronze, aluminum, or another type of alloy? Know this to select the right conductor. Also consider no of conductors, solid or stranded.
• Cross Sectional Area- It defines the current carrying capacity of your cable. A larger cross-section area results in lower resistance per foot when the type of wire is the same. It is usually expressed in square inches, square millimeters.
| Cross sectional area v/s Current carrying capacity per core | |||
| COPPER | ALUMINIUM | ||
| Cable Size in (Sq.mm) | Current in Amps | Cable Size in (Sq.mm) | Current in Amps |
| 1 | 17 | 4 | 16 |
| 2.5 | 30 | 6 | 20 |
| 4 | 40 | 10 | 25 |
| 6 | 51 | 16 | 35 |
| 10 | 69 | 25 | 43 |
| 16 | 91 | 35 | 65 |
| 25 | 119 | 50 | 80 |
| 35 | 146 | 70 | 91 |
| 50 | 175 | 95 | 120 |
| 70 | 221 | 120 | 153 |
| 95 | 265 | 150 | 188 |
| 120 | 305 | 185 | 230 |
| 150 | 334 | 240 | 270 |
| 300 | 532 | 300 | 340 |
• Voltage Rating- The voltage rating of a cable refers to the maximum voltage to which it may be connected (and have running through it).If the voltage rating is exceeded, the insulation between cable cores, or between a cable core and earth, may break down and cause a short circuit or a fire. Usually rating is mentioned in RMS value.
A typical voltage rating is 0.6/1 kV. This means that a cable with this rating is capable of withstanding a voltage of 0.6 kV (600 volts RMS) between the conductor and earth, and 1 kV (1000 V RMS) between adjacent conductors.
• Temperature rating- The temperature rating of a cable is the maximum temperature at which it may be operated without damaging the insulation. A typical temperature rating for general wiring in a domestic installation is 75oC. There are special cables available that have insulation capable of withstanding higher temperatures. For example, V105 PVC cable has a maximum temperature rating of 105oC.
• Standards- Standards will be as per Classification Society Rules and Regulation. In general electric cables used onboard are of JIS standard(Japanese Industrial Standard) except for antenna, thermometer, etc shall be of manufacturer standard. Discussed in detail below.
STRUCTURE OF MARINE CABLE
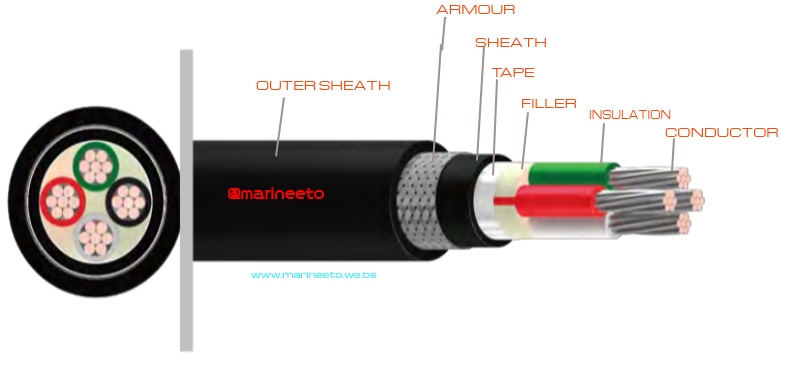
- Conductors also known as the core of the cable consist of single conductor or stranded conductor made up of aluminum or copper because of their high electrical conductivity.
- Insulation is provided to prevent shorting of conductor.commonly used dielectric in power cables is impregnated paper, butyl rubber, polyvinyl chloride cable, polyethylene, cross-linked polyethylene.
- Filler provides a circular shape to the cable. It also has several functions and reducing friction and heat which can degrade your wiring over time.
- Tape is used to hold conductors and fillers firmly so that manufacturing becomes easier and bind together to desired shape. It also expels air pockets.
- Sheathing also known as beading is provided to protect cable insulation from moisture. The material used for the inner sheath should be nonmagnetic material.
- Armouring is the process in which layers of galvanized steel wires or two layers of metal tape are applied over sheath for protecting it from mechanical damage. It has to be earthed because of induction EMF can be generated in Armour.
- Outer Sheath is provided for overall protection from dirt, oil, temperature, moisture, etc and also for better mechanical strength.
TYPES OF CABLE USED ONBOARD SHIP
Cables are classified based on their current carrying capacity, voltage, type of application. Here is a list of classification of marine cables used onboard ship.
POWER CABLE
The power cable is an assembly of 1 or more conductors used to transmit electric power. This cable comes armoured or unarmoured. These cables are mainly used in the Power distribution in the Feeder panel, Starter panel, etc.

CONTROL CABLE
These are flexible copper or aluminum single core PVC cable also known as the wire used for wiring in the control circuit, lighting accessories, etc. (wire is a single conductor, multiple conductors are called cable)

CO-AXIAL CABLE
Coaxial cables, commonly called coax, are copper cables with metal shielding designed to provide immunity against noise and greater bandwidth. Coax can transmit signals over larger distances at a higher speed as compared to twisted pair cables.
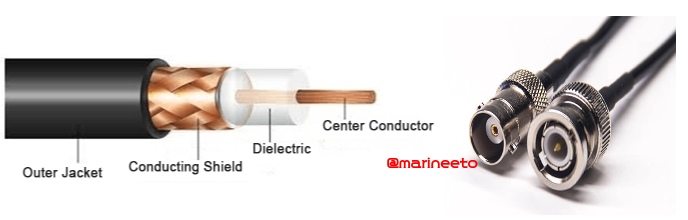
These cables are used to connect between Antenna and Transceiver, RADARS, Satellite Phones, etc.
ETHERNET CABLES
Popular type network cable used to connect a computer, modem, routers for high-speed digital data transmission. These cables are twisted pair cables and classified as CAT5, CAT5e, CAT6, CAT6a, CAT7. It comes with standard RJ45 Male Connector at both ends.

Onboard ship CAT5 used for Computers, Routers, Printers, PLC, ECDIS, RADAR and other Navigational Equipment.
INSTRUMENTATION CABLES
Instrumentation cables are multiple conductor cables that convey low energy electrical signals used for monitoring or controlling electrical power systems and their associated processes.

Onboard Ship it is used to wiring of sensors, fire detectors, HART(4-20ma signal), Serial Communication(RS-232, RS-485), etc.
RIBBON CABLES
A ribbon cable is a flat, thin cable composed of multiple small-grade cables placed parallel to each other. With each core situated side by side, they form a wide-flat cable resembling a piece of ribbon, hence its name. This type of cable is mostly used in electronic systems that require multiple data buses to link internal peripherals.

You can find these types of cables in the Complex electronics system in PLC cards, Alarm Monitoring System Cards, Navigational Equipments, Computer Peripherals.
How to read Marine Cable type and Symbol?
The below figure and table show JIS standard detailed explanation of prefixes and suffixes used in cable specification.

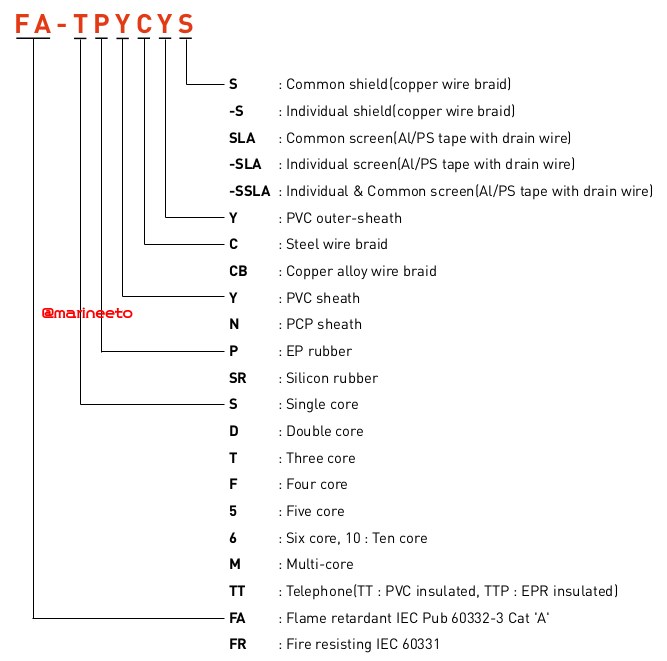
Similar examples are given below for better understanding.
| 0.6/1 kV TYPC-10 | 0.6/1 kV, Flame resisting, Three core, EP rubber insulated, PVC sheathed, Steel wire braided and 10mm2 nominal sectional area cable. |
| 0.6/1 kV DYPCY-6 | 0.6/1 kV, Flame resisting, Double core, EP rubber insulated, PVC sheathed, Steel wire braided, PVC protective covered and 6mm2 nominal sectional area cable. |
| FA 250V MPYC-7 | 250 V, Flame retardant, Multi core (7 cores), EP rubber insulated, PVC sheathed, Steel wire braided and 1 mm2 nominal sectional area cable. |
| 250V MPYCYS-4 | 250 V, Flame resisting, Multi core (4 cores), EP rubber insulated, PVC sheathed, Steel wire braided, PVC protective covered and 1mm2 nominal sectional area cable with common shield. |
| 0.6/1 kV TPNP-1 | 0.6/1kV, Three cores, EP rubber insulated, PCP sheathed and 1 mm2 nominal sectional area flexible cable. |
What are Hazards in case Electric cable catch fire?
Cable is made up of metal, rubber and plastic. When it catches fire it generates very dense black smoke with an irritating smell similar to burning tyre. Insulation and Sheathing which contains PVC generates Hydrochloric gas which can irritate the lungs, causing a cough and shortness of breath.
CONCLUSION
Manufacturing standard and construction may slightly differ but the concept used is the same. Cross-sectional area v/s current carrying capacity is approximated table for certain resistance, resistivity changes as per the length of the cable and temperature can also affect. Consider these points while ordering cable onboard for replacement or new installation. I hope this post will help you.
REFERENCE
- MYOUNGIN ELECTRIC WIRE CO.LTD www.micable.co.kr
- Meridian Cable Assemblies www.meridiancableassemblies.com
LIKE POST? PLEASE SHARE
















very good article. we need this article for teaching.
Thanks for providing great informative and looking beautiful blog. Keep it up.
GOOD MORNING
I am kindly very happy to find myself dropping my comments.
I think I will learn more on this platform.
Keep learning spread words to make others also grow.
Good luck & great career ahead.