ULTIMATE BEARING GUIDE & FACTS FOR ETO
The bearing reduces friction & serves smoother rotation for rotating parts of the machinery. Do you know the different types of bearing, their numbering nomenclature, handling bearing? If your answer is NO here is an ultimate bearing guide and facts about bearing that every ETO must know.
Let us start with the basic from different components & types of bearing used.
PARTS OF BEARING
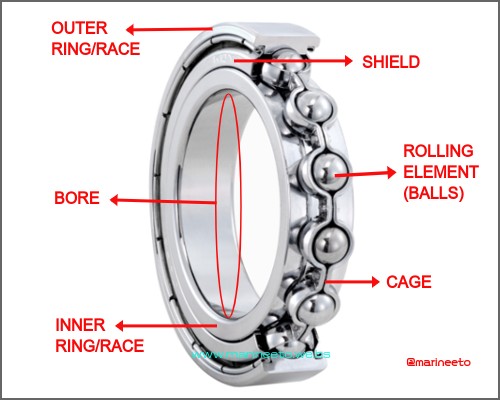
- INNER RACE: This is the part that is mounted on the rotating shaft and tends to rotate the shaft.
- OUTER RACE: This is the part that is mounted to the housing and is stationary. This also serves as a means for transferring the loads from the bearing to the housing.
- ROLLING ELEMENT: These are the elements that carry the load distributing it throughout the raceways. They tend to rotate about the inner race, but not at the speed the inner race rotates. It is something like the relation between the earth and the moon.
- CAGE: This is an important element in the bearing. This acts as a barrier between the balls preventing them from bumping into each other.
- SHIELD: It is designed to obstruct larger particles from entering the bearing, to prevent contamination & keep the grease inside the bearing.
What are the different types of Bearing?
- Plain Bearings
- Ball Bearings
- Roller Bearings
- Fluid Bearings
- Magnetic Bearings
Most commonly used bearing onboard ship is Ball Bearing. The below figure shows different types of ball bearing,

- Self-aligning ball bearing: bearings are manufactured with two rows of balls and one continuous spherical raceway in the outer ring. This allows for the limited misalignment of the shaft and housing.
- Deep groove ball bearing: radial bearings are manufactured as open type bearings for oil or grease lubrication. They are also available with metal shields and/or seals for use where moderate contamination is present in the operation.
- Thrust ball bearing: Thrust ball bearings are classified into those with flat seats or aligning seats depending on the shape of the outer ring seat (housing washer). They can sustain axial loads but no radial loads. For Single-Direction Thrust Ball Bearings, pressed steel cages and machined brass cages have usually used the cages in Double-Direction Thrust Ball Bearings are the same as those in Single-Direction Thrust Ball Bearings of the same diameter series.
- Angular contact ball bearing: bearings are single row types used where radial and thrust loads are combined in the same application. They provide sufficient internal clearances to assume a specific contact angle under thrust loading and are available with angles of 15°, 30°, and 40°.
HOW TO READ BEARING NOMENCLATURE?
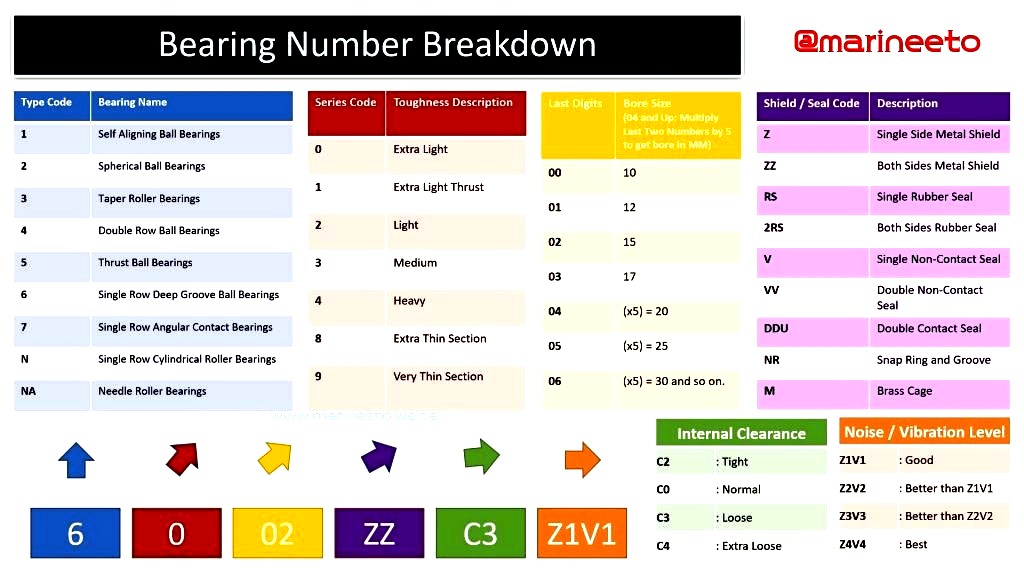
The number and letter combinations have the following meaning:
- The first digit or letter or combination of letters identifies the bearing type and eventually a basic variant. For Example: In bearing 6200, the first digit indicates that it is a Deep Groove Ball Bearing.
- The following two digits identify the ISO dimension series. The first digit indicates the width or height series (dimensions B, T, or H). The second digit identifies the diameter series (dimension D).
- The last two digits of the basic designation identify the size code of the bearing bore. The size code multiplied by 5 gives the bore diameter (d) in mm.
- The fifth letter in bearing nomenclature indicates the type of shields/seal used.
- The Sixth letter tells the internal clearance. This is very important while choosing the ball bearing for the right application.
| C2 | It is less than normal so the bearing is tighter (designed for slower-moving more precise applications that require little or no play in the bearings where the temperature remains fairly constant. |
| C3 | It is designed for hot running environments; Hot water circulation motor, HFO supply motor, engines, etc. where the bearing temp could reach 100° or more. |
| C4 | It is used in more extreme temperature applications and higher speed environments. |
| C5 | It has the highest clearance bearing available, are extremely loose to start, and can knock until at operating speeds and temperature. |
BEARING HANDLING TIPS
There are few tips for handling bearing that you can follow to ensure longer life span, as follows:
STOWAGE
Store at a secure location where there is less water & dust ingress so that its free from corrosion.
LUBRICATION
Bearing comes pre-lubricated from the manufacturer, please do not remove the lubrication coating, Use correct lube oil/grease recommended by the maker for routine maintenance for motor bearing.
MOUNTING & REMOVAL BEARING
Inserting/Removing bearing has to be done carefully. The bearing should be mounted slowly with care, by using a fixture to apply force evenly to the bearing. When mounting bearing apply pressure to inner ring only, Similarly while removing apply pressure to the outer ring of the bearing. Some methods of mounting/removal are listed below,
1.MOUNTING/REMOVING USING HYDRAULIC PRESS & HYDRAULIC JACK
The bearing can be inserted into the shaft by using a Hydraulic press, Similarly, it can be removed by a hydraulic jack.
2. HOT MOUNTING
In this method, the bearing is heated up to 100°C, because metal expands on heating due to which only less pressure can be applied while fitting it to the shaft. This method is suitable for large bearing where more pressure is required to fit. Heat can be applied by Heating in Oil or Induction heating. Remember never to heat more than 120°C, Overheating can alter diameter or cause hardness.
3. MOUNTING/REMOVAL USING BEARING TOOL KIT
This is one of the most common & widely used method onboard ships for mounting/removing bearing but this method needs more force & the risk of damaging bearing. The commonly used tools are a Bearing puller, Hammer, Impact ring & Sleeves (correct size pipe can also be used).
PRO-TIP
How to remove seized bearing?
Heat the bearing using a hot air blower, applying de-rust aerosols like WD40 & start pulling using a 3-arm puller for better pulling force, still unsuccessful? use a hydraulic puller.
If a hydraulic puller not available, cut the outer race/ring & cage, Now the remaining inner race/ring can be removed easily by applying heat & cutting it slightly, hit using hammer & chisel slowly until it loosens and can be removed.
Remember, be very careful while handling tools & do not overheat too much, if the shaft is damaged the entire process of removing the bearing is a failure.
WATCH VIDEO
REFERENCES
- Simply Bearings https://simplybearings.co.uk/
- NSK Bearing https://www.nsk.com/
- HCH Bearing https://www.hchbearingamericas.com/
- PIC CREDITS: JVN BEARING
ALSO READ: ALTERNATOR MAINTENANCE GUIDE INDUCTION MOTOR QnA
More to add? Share your thoughts to mail@marineeto.we.bs
LIKE POST? PLEASE SHARE















very great, refreshing and improving knowledge