EGCS – DETAILED OVERVIEW
To ensure compliance with IMO regulations, most of the modern fleet is equipped with EGCS (Exhaust Gas Cleaning System). The main purpose of EGCS is to reduce SOx & NOx from exhaust gases that are generated from Main Engine, Auxilary Engine, and other machinery, Since IMO 2020 limited sulphur content to 0.50% globally and 0.10 % m/m in ECAs (Emission Control Areas) for the merchant fleet. EGCS employs Scrubber to remove SOx components.
TYPES OF EGCS
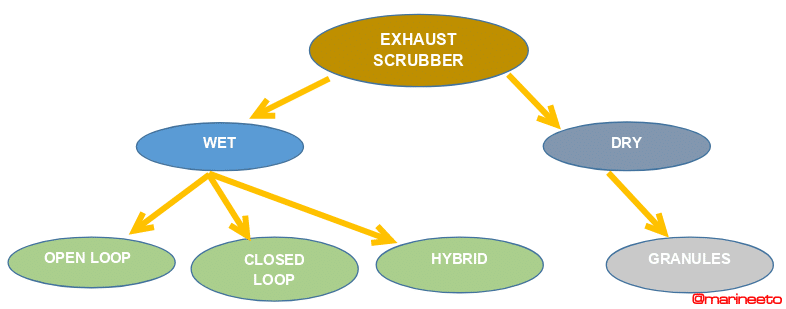
DRY SCRUBBER: Water or any cleaning liquids are not used in the scrubber, instead pellets or granules are used for removing SOx content. Example: Hydrated Lime, Fabric Filter, etc. The chemical reagent reacts to neutralize the harmful compounds.
WET SCRUBBER: Sea water or Fresh water is used in the scrubber to remove SOx content. They are further classified based on their design, they are,
- OPEN-LOOP EGCS, seawater is used for scrubbing, and effluents (wash water) are discharged to sea.
- CLOSED-LOOP EGCS, freshwater & alkaline chemicals is used for scrubbing. effluents are not discharged to sea, they are recirculated & treated with chemicals to neutralize sulphur, and contaminants are stored for shore disposal.
- HYBRID EGCS can operate with both freshwater & seawater and also can be used as a closed or open loop.
NOTE: The Diverting Dampers may be provided with EGCS to operate on EGCS mode or Bypass-mode while using Low-Sulphur fuels.
COMPARISION OF WET & DRY SCRUBBER
| PARAMETER | WET SCRUBBER | DRY SCRUBBER |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Lower temperature because exhaust gas is cooled by fresh or seawater | Higher temperature because exhaust gas is not cooled compared to wet scrubber. |
| Power | Power consumption is high, scrubber pump consumes a lot of electricity. Booster/Recirculation pumps also operate for short intervals. | Power consumption is low, No scrubber pump, Booster/Recirculation pumps. |
| Scrubbing Element | Seawater, Freshwater, or both is used. | Filters, Limestone Granules, or desulphurizing agent like Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3) is used. |
| Disposal | Scrubbing liquid can be discharged to sea, But the pH level of water has to be maintained at all times to prevent damage to the marine environment. | Scrubbing elements are mostly chemicals, and cannot be discharged to sea. Requires storage & off-land ashore. |
| Installation | Quite a complex installation, modification of sea-chest may employ. | Installation is easier compared to the wet scrubber. |
In this post, we will discuss Open-loop EGCS, Closed-loop EGCS & Dry Scrubbers.
1. OPEN-LOOP EGCS
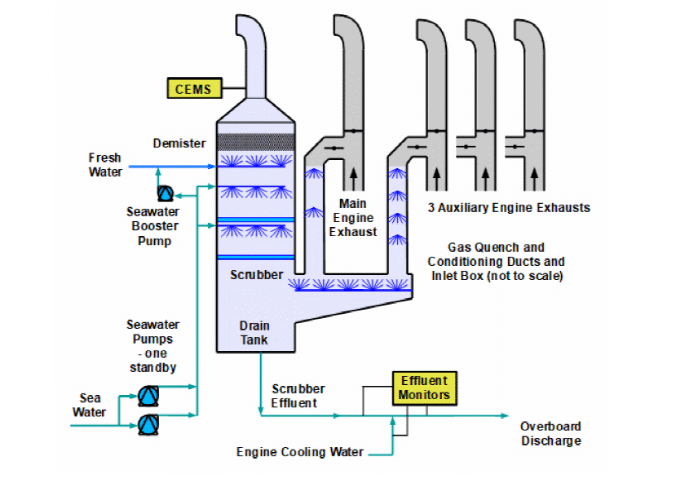
In the below figure, seawater is pumped to the scrubber, and seawater absorbs SOx with its natural alkalinity & partially neutralizes it. The water draining(output) from the scrubber has a pH above 3.0 & discharged overboard through an Effluent monitor, further neutralized using seawater if the pH is below 3.0.
The major components are:
SEAWATER PUMPS: To supply water for spray inside the scrubber. These pumps are VFD controlled by PLC. The flow rate depends on setpoints. Sea water booster pumps are also provided to prevent scales & clean demister vanes.
FRESHWATER PUMP: Used for rinsing while stopping the system to remove salt deposits.
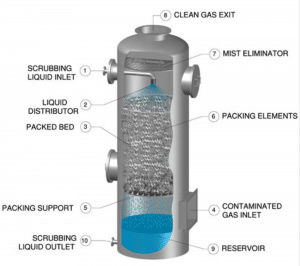
SCRUBBER: Liquid or Solid particles are removed by water from the exhaust gas. It consists of water spray & mist eliminator (demister).
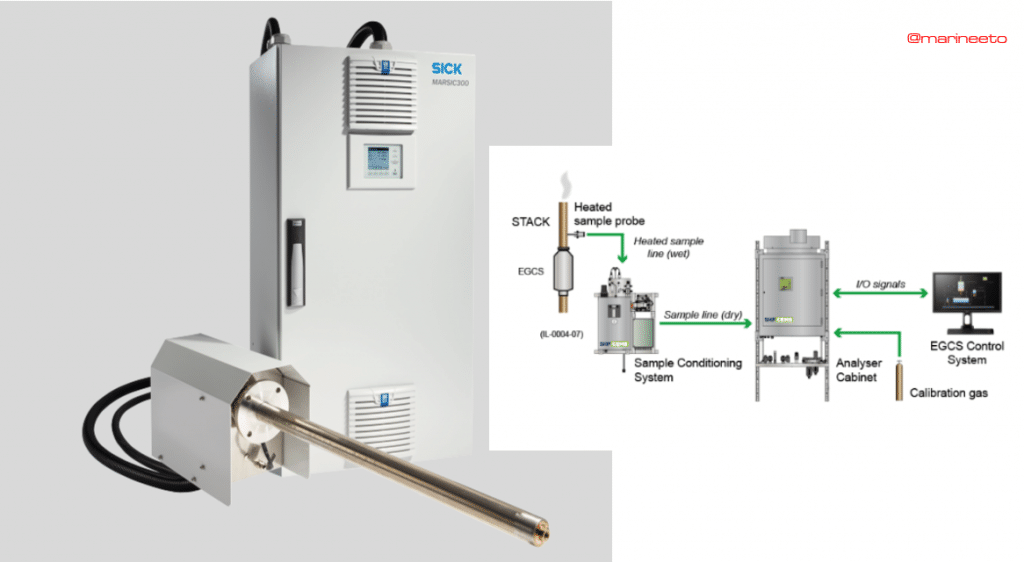
CEMS: Continuous Emission Monitoring System is an important component of EGCS, It measures the exact content of SOx & CO2 in emission gases after scrubbing.
EFFLUENT MONITOR: This is also known as WWMS (Wash Water Monitoring System). This is a standalone system that monitors pH, PAH (Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons), and the Turbidity of scrubber effluent (Washed water from the scrubber that is discharged to sea).
2. CLOSED-LOOP EGCS
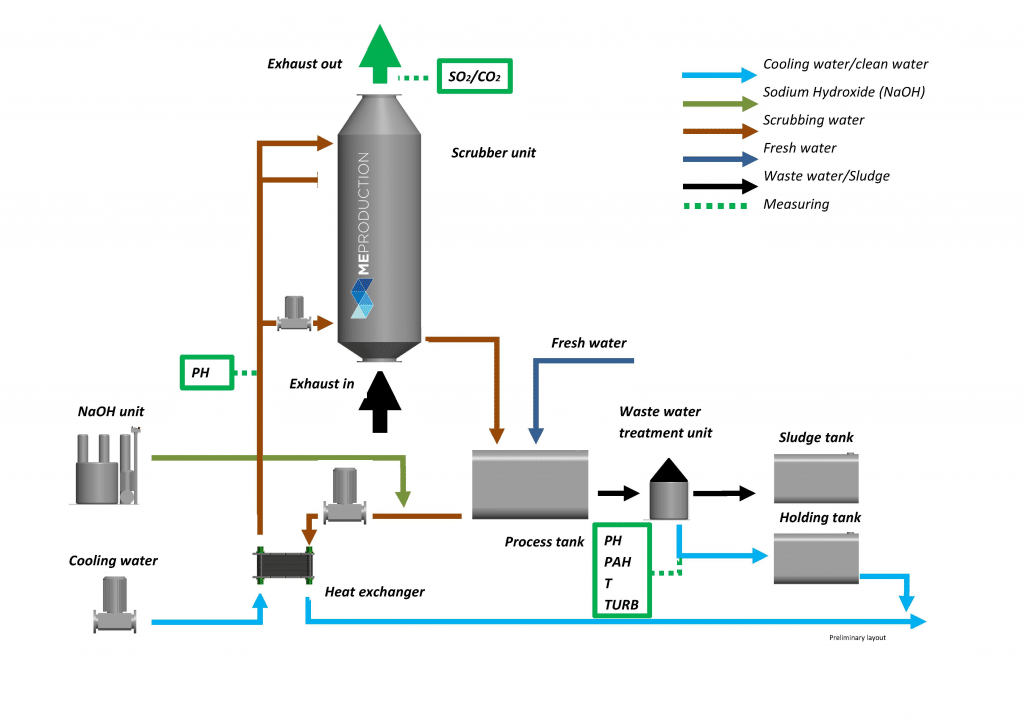
The closed-loop has similar components compared to open loop scrubber additionally, The system has Chemical Dosing Unit, Process Tank, Heat Exchanger, and Wastewater treatment unit.
Fresh water is sprayed into the scrubber with a neutralizing agent (NaOH, Caustic Soda). The washed water (effluent) is passed to the process tank where it is recirculated to the scrubber & evaporative loss is replaced by adding fresh water. The hot recirculation water is cooled by a heat exchanger. The small quantity of water from the process tank is further treated in the treatment unit & separated into a sludge tank & holding tank.
3. DRY SCRUBBER
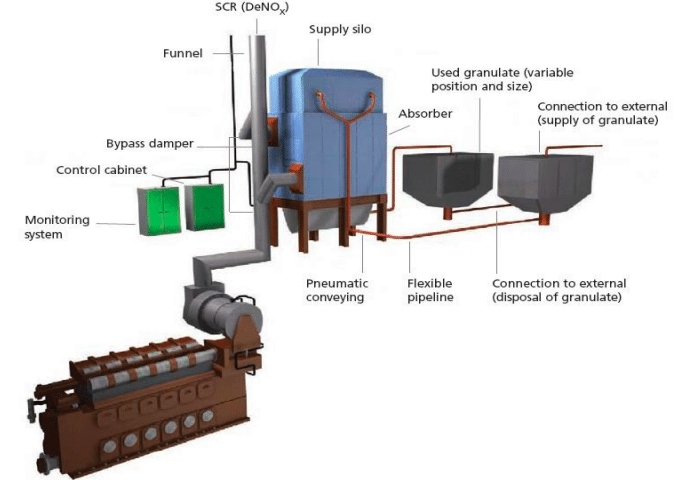
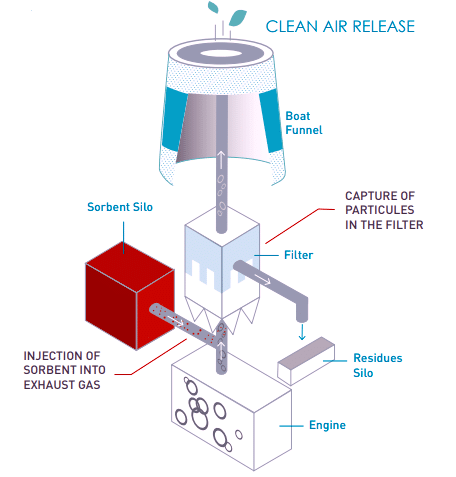
No seawater or freshwater is used in the dry scrubber, Calcium hydroxide granules are used to remove SOx contents. Granulates drop slowly from a supply silo through a two-stage construction of an absorber to a discharge system under gravity.
When exhaust gas passes perpendicularly through an absorber full of calcium hydroxide granulates, the first stage of granulates, located below the second one, is used as a sacrificial layer for removing the rough sooty particles and other residuals, in a similar way to particulate matter filter. The second stage of granulates, meeting the exhaust gas while still fresh, is where the desulphurization occurs and the chemical reactions scrub away the SO2 and SO3. The used granulates, which are turned into gypsum with the retained spherical form, are then conveyed by the discharge system to a granulate storage onboard.
ROLES OF ETO
- Make sure all measuring instrument is working satisfactorily.
- Ensure all cabinet filters for cooling control panels is free of dust & cooling fans are operating satisfactorily.
- Schedule maintenance on optical sensors as per maker-recommended intervals & procedures.
- Check operation & feedback of all valves, and overhaul the defective directional solenoid valves.
- pH, PAH, and Turbidity sensors must be calibrated as per maker suggested time interval or request shore calibration, to avoid erratic measurements while the plant is in operation.
- Test critical alarms & trips, emergency stops as per company PMS (preventive maintenance system).
- Maintain correct ROB of important spare parts.
DRAWBACKS
- Expensive to install, and consume a lot of space, especially retrofitting.
- Measuring Instruments & Equipment needs expensive shore maintenance annually.
- Scrubbers do not remove NOx, and CO2 content completely.
- Seawater scrubber pipelines start leaking over a period of time.
- While the plant is in operation, Any failure or fault in the system causing the stop of the system must be rectified in a short span of time, If not changeover fuel to MGO to comply with IMO requirements.
REFERENCES
- Solvair www.solvay.com/solvair-marine
- Wartsila Exhaust Solution www.wartsila.com/exhaust-treatment
- EGCSA www.egcsa.com/technical-reference/
- Pacific Green www.pacificgreen-marine.com/
Anything Missing? Please share your feedback.















Good day.
Please give us your e-mail address. We have an enquiry for ships spares that we will send to you as soon we have the address. Please reply today.
We can make the PAH sensor test the water ,wish you reply us